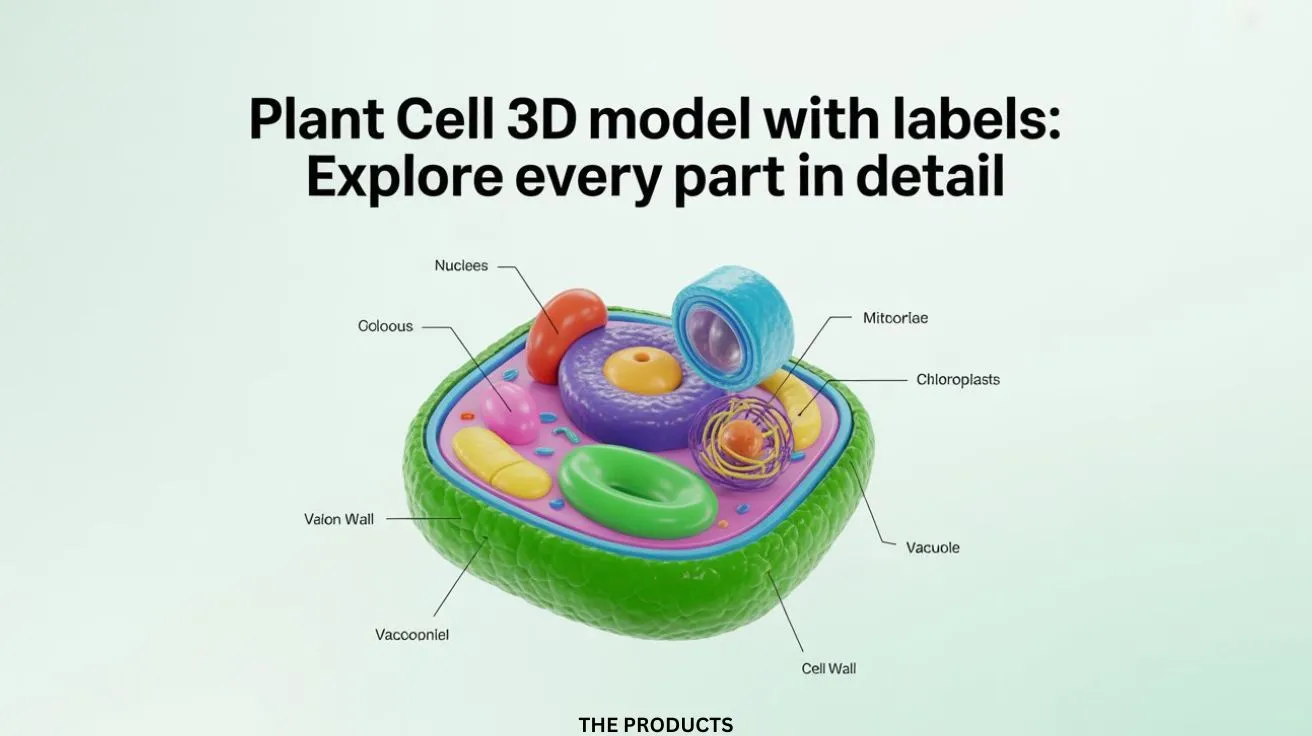
Understanding plant cells is easier and far more engaging with a 3D plant cell model with labels. This visual representation allows students, teachers, and science enthusiasts to explore the structure and functions of each organelle clearly. From the cell wall to chloroplasts, a 3D model gives a comprehensive view of how plant cells operate, making biology more interactive and fun.
What Is a Plant Cell?
A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell forming the basic unit of plants. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a rigid cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a large vacuole that stores nutrients and water. Grasping the functions and positions of these parts is essential for students learning about plant anatomy, and a 3D model makes it much easier to visualize.
The 3D Plant Cell Model
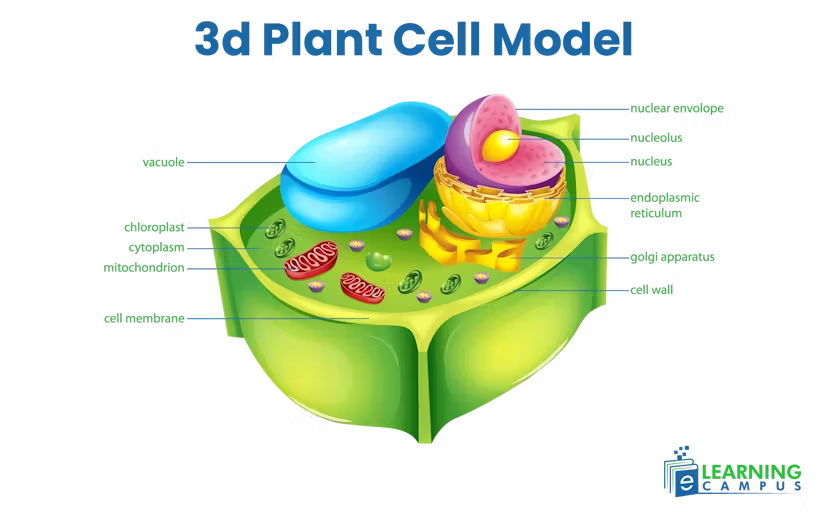
A 3D plant cell model brings the complex structure of plant cells to life. Unlike flat diagrams, the three-dimensional view allows learners to see the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuole in their relative positions. Labels on the model help students memorize organelle names and understand their roles in a more intuitive way. Using this model can enhance comprehension, improve exam performance, and make learning plant biology engaging.
Functions of Plant Cell Parts
The cell wall is the outer layer that provides mechanical support, maintaining the plant’s shape and rigidity while acting as a semi-permeable barrier for water and nutrients. Beneath it, the cell membrane controls the movement of substances, separating the cytoplasm from the outside environment and protecting the cell from damage.
At the center, the nucleus serves as the control hub, containing DNA and regulating cell activities like protein synthesis, cell growth, and division. Chloroplasts perform photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy and producing glucose and oxygen. The vacuole, usually the largest organelle in plant cells, stores water, nutrients, and waste while maintaining turgor pressure essential for cell structure. Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, generate energy in the form of ATP, supporting all cellular functions.
Cell Wall
The cell wall is the outermost layer of a plant cell, primarily made of cellulose. Functions:
- Provides mechanical protection
- Maintains cell shape and rigidity
- Acts as a semi-permeable barrier for water and nutrients
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, located beneath the cell wall, is a lipid bilayer that controls the movement of substances. Functions:
- Separates the cytoplasm from the cell wall
- Regulates transport of molecules
- Protects the cell from external damage
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center containing DNA and regulating cell activities. Functions:
- Controls protein synthesis
- Coordinates cell growth and division
- Stores genetic material
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy. Functions:
- Produces glucose during the Calvin cycle
- Releases oxygen
- Synthesizes amino acids and lipids
Vacuole
The vacuole stores water, nutrients, and waste. In plant cells, it is larger than in animal cells. Functions:
- Maintains turgor pressure
- Stores essential compounds
- Helps in cell growth and detoxification
Mitochondria
Known as the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria generate energy for cell functions. Functions:
- Produces ATP for energy
- Stores calcium for signaling
- Regulates cell growth and division
READ MORE >>> Refrigerator Repair NYC – Fast, Reliable Service in New York City
How to Use a Plant Cell 3D Model with Labels
The model allows students to explore each organelle in a realistic way. By examining labeled diagrams, learners can memorize the names and functions of each part while understanding how they interact within the cell. Combining the model with textbooks or online resources can provide a complete learning experience, making it ideal for classroom study or home learning.
Advantages of 3D Plant Cell Models
Using a 3D plant cell model transforms the learning process. It provides visual clarity for complex structures, improving retention and understanding. The interactive nature of the model keeps students engaged and makes studying plant cell organelles more enjoyable. Whether it’s for school assignments, exams, or simply exploring biology, a labeled 3D model is an invaluable tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Make 3D Models of Plant and Animal Cells?
Creating 3D models of plant and animal cells can be done using simple materials like clay, foam, or cardboard for classroom projects. For more advanced or accurate models, you can use 3D modeling software such as Blender, Tinkercad, or SketchUp. Label each organelle clearly and follow the actual structure of the cell to make it realistic. Interactive 3D models help students understand the position and function of organelles more effectively.
Are 3D Printed Plant Cell Models Available?
Yes, 3D printed plant cell models are widely available online and in educational stores. These models come pre-labeled or blank, allowing students and teachers to explore organelles like the nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, vacuole, and cell wall in 3D. They are highly beneficial for classrooms, labs, and even home study.
What Does a 3D Plant Cell Model Show?
A 3D plant cell model displays the complete structure of a plant cell, including the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, vacuole, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. It visually explains the function of each organelle and their spatial arrangement, making it easier to learn compared to 2D diagrams. Some models also show microscopic features, like ribosomes or Golgi apparatus, for advanced learning.
Can You 3D Print Cell Models?
Absolutely! With access to a 3D printer and the right 3D design files, you can print both plant and animal cell models. These models can be scaled to any size, labeled, and colored to highlight organelles. Open-source platforms often provide downloadable 3D models specifically designed for educational use.
Is Anything Illegal to 3D Print?
Yes, there are restrictions on certain items. It is illegal to 3D print weapons, counterfeit goods, or copyrighted products without permission. Always follow local laws and regulations when creating or printing 3D models to ensure safety and legality.
Can AI Make 3D Printable Models?
Yes, AI tools and software can generate 3D printable models from designs or sketches. AI can assist in automating the creation of cell models by converting 2D diagrams into accurate 3D structures, complete with labels for educational purposes. These AI-generated models can then be exported in formats compatible with most 3D printers.
Conclusion
A plant cell 3D model with labels is a powerful learning tool for students, teachers, and science enthusiasts. By providing a clear visual representation of each organelle, it enhances comprehension, retention, and interest in plant biology. Exploring the model allows learners to understand the function of every part of the cell, making plant cell biology both educational and engaging.